
PUBLICATIONS
Livres scientifiques
Monographies
Publications nationales indexées
Publications Internationales indexées
LES PATHOLOGIES DE LA MUQUEUSE BUCCALE (CDP) 2024
Collection Memento
Par : Lotfi Benslama
Voici un ouvrage qui sera fort utile à tous ceux qui s'intéressent à la muqueuse orale : stomatologistes, chirurgiens oraux, chirurgiens maxillo-faciaux, dermatologues, otorhinolaryngologistes, chirurgiens-dentistes.
Son principe est d'illustrer, à partir de lésions élémentaires déclinées selon leur description basique, la quasi-totalité des pathologies observées à la muqueuse orale : de l'aphte bénin à la verrue, aux maladies de système ou aux effets iatrogènes jusqu'aux cancers avec leurs présentations multiples.
Pour chaque affection, un texte de quelques lignes décrit, différencie, recadre et esquisse une conduite à tenir ou une thérapeutique. Ce manuel est d'usage quotidien chez les praticiens qui examinent et observent la bouche.
Voir + : Publications présentées par la SFSCMFCO
Pésentation de l'auteur : Le Dr Lotfi Benslama est chirurgien stomatologiste et maxillo-facial...
Au sommaire : Les pathologies de la muqueuse buccale

CANCERS DE LA CAVITE BUCCALE (JPIO)
Du diagnostic aux applications thérapeutiques
Par : H Tarragano, B Illouz, F Moyal, P Missika, L Ben Slama
Les cancers de la cavité buccale regroupent l'ensemble des tumeurs malignes développées au niveau de la muqueuse de recouvrement de la bouche et des lèvres.
Les cancers buccaux sont paradoxalement caractérisés par un dépistage le plus souvent tardif, bien que la cavité buccale constitue, avec le revêtement cutané, l'une des seules régions anatomiques de l'organisme « explorable » sans dispositifs médicaux invasifs. L'absence de dépistage précoce peut s'expliquer tant par le manque d'intérêt porté par de nombreux praticiens pour ces pathologies que par un réel manque d'information (et de formation) de ces derniers.
L'objectif ectif de cet ouvrage est donc de décrire la démarche clinique en carcinologie orale, étape par étape, de l'anamnèse jusqu'au diagnostic et à la mise en route des thérapeutiques médico-chirurgicales, en se référant aux données les plus récentes concernant la prise en charge des cancers buccaux.
Chaque chapitre se complète d'une série d'arbres décisionnels résumant l'ensemble des éléments abordés, permettant une consultation rapide et pratique dans l'exercice quotidien. Les notions de base indispensables à toute démarche clinique (données épidémiologiques, rappels anatomopathologiques, facteurs étiologiques...) sont regroupées au sein d'un seul et même chapitre.
En fin d'ouvrage, les auteurs exposent les différentes stratégies de prise en charge odontostomatologique du patient cancéreux, notamment celles concernant la gestion des effets indésirables et des séquelles de la radiothérapie et de la chirurgie d'exérèse carcinologique. La prévention, basée sur la connaissance des facteurs de risque, est également abordée afin de fournir au lecteur une approche complète de la carcinologie orale.
Ce livre s'adresse essentiellement aux chirurgiens dentistes et aux spécialistes en stomatologie et chirurgie maxillo-faciale, mais aussi aux oto-rhino-laryngologistes ainsi qu'aux étudiants en médecine et en chirurgie dentaire.
Il est le fruit d'une étroite collaboration entre praticiens chirurgiens dentistes et chirurgiens maxillo-faciaux, exerçant dans le domaine hospitalo-universitaire. Il intéressera également tous les dermatologues, directement concernés par la détection des cancers des lèvres.
Voir + : Cancers de la cavité buccale. CDP. Collection : JPIO
PANORAMA DES PRINCIPALES AFFECTIONS DE LA MUQUEUSE BUCCALE
Par Lotfi Benslama
- I - Les lésions blanches
- II - Les lésions érythémateuses
- III - Les lésions pigmentées
- VI - Les ulcérations
- V - Les nodules
Voir : Panorama des principales affections de la muqueuse buccale

TRAITÉ DE MÉDECINE
Par Pierre Godeau, Serge Herson, Jean-Charles Piette
Ouvrage de référence indispensable de la médecine interne française. Le lecteur va pouvoir trouver de nouvelles sections (regroupant une centaine de nouveaux chapitres) comme la biologie moléculaire, le sida, la gériatrie, les pathologies musculaires et vasculaires, les transplantations d'organes ou encore la nutrition. Les autres chapitres ont été actualisés et se présentent toujours selon un plan identique : étiopathogénie, physiopathologie, examen clinique, examens complémentaires et stratégie d'exploration, diagnostic, évolution, thérapeutiques et pronostic de la maladie.
Pierre Godeau, Jean-Charles Piette et Serge Herson sont des personnalités phares en médecine interne ; ils ont travaillé en étroite collaboration avec Z.Amoura, Z.Boutin, P.Cacoub, P.Cherin, C.Francès, T.Papo, B.Wechsler, également personnalités éminentes dans la discipline. Ensemble, ils ont coordonné le travail de 600 rédacteurs tous choisis pour leur compétence et leur notoriété.


PHOTOGRAPHIE NUMÉRIQUE MÉDICALE ET DENTAIRE
Par Lotfi Ben Slama, Cyrille Chossegros
Les nouvelles dispositions réglementaires et médico-légales ainsi que la bonne tenue du dossier du patient imposent de plus en plus souvent l'utilisation de la photographie numérique.
Les auteurs, qui ont recensé et résolu nombre de problèmes qui peuvent se poser dans cette pratique particulière de la photographie numérique, se proposent de partager leur expérience dans un ouvrage entièrement en quadrichromie, richement illustré avec de nombreux schémas explicatifs et d'exemples des bonnes pratiques et des erreurs à éviter.
Voir + : Photographie numérique médicale et dentaire

PATHOLOGIES DE LA MUQUEUSE BUCCALE
Par Henri SZPIRGLAS , Lotfi BEN SLAMA
Cet atlas, accompagné de son CD-ROM, réalisé par les docteurs Szpirglas et Ben Slama représente à la fois une innovation et un progrès important en stomatologie.
La cavité buccale est souvent telle une fenêtre s'ouvrant sur l'organisme et les maladies systémiques, pouvant à la fois refléter l'atteinte d'organes éloignés ou être à la source de certaines lésions distantes. De la même façon, une connaissance approfondie du complexe orofacial et l'aptitude à reconnaître et caractériser les anomalies de la cavité buccale sont des facteurs essentiels dans maintes disciplines des sciences de la santé.
Voir + : Pathologies de la muqueuse buccale

AIME - Les Assises pour l'Innovation en Médecine Esthétique
Intervention de Lotfi BEN SLAMA.
Thème : les microgreffes de cheveux. Innovations. La FUT et la FUE
AIME : Les dernières techniques d'injection, les nouvelles technologies biologiques et physiques, les domaines novateurs telles la médecine esthétique génitale et les réalités augmentées et virtuelles et l'actualité de la médecine anti-âge
Voir + : AIME
Voir + : Programme de la journée
Voir + : Microgreffes de cheveux - FUT et FUE


TRIBUNES
Par Lotfi BEN SLAMA.
Voir + : Index des tribunes
- Greffes osseuses autologues, allogreffes et biomatériaux : quelle place pour les greffes osseuses allogéniques et pour les "biomatériaux" en chirurgie maxillo-faciale, et plus particulièrement en chirurgie pré-implantaire
Voir + : Greffes osseuses autologues, allogreffes et biomatériaux
- Risque d'endocardite infectieuse et implants dentaires . L'endocardite infectieuse, complication redoutable des foyers infectieux bucco-dentaires, quoique rare, est mortelle dans plus de 25 % des cas. Et la péri-implantite ?...
Voir + : Risque d'endocardite infectieuse et implants dentaires
- Implants et vitamine D. L'extra-ordinaire épopée de la vitamine D et autres en implantologie dentaire. Une nécessaire évolution
Voir + : Implants et vitamine D

EXTRAITS DES PUBLICATIONS.
Ci-dessous : références et liste non exhaustive
Publications nationales et internationales indexées
LA PAPULOSE LYMPHOMATOÏDE (PL)
Par Lotfi Ben Slama ; C.V. Andre ; Frédéric Charlotte ; Patrick Goudot
La papulose lymphomatoïde (PL) est une dermatose chronique évoluant par poussées. Elle est classée par le WHO-EORTC dans les lymphoproliférations T-cutanées primitives CD30+. L’atteinte muqueuse est rare (15 cas décrits). Nous rapportons 2 nouveaux cas de PL de la muqueuse buccale en absence d’atteinte cutanée.
Voir + : www.researchgate.net
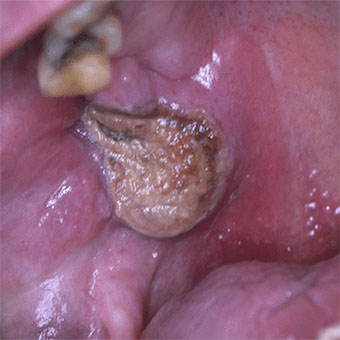
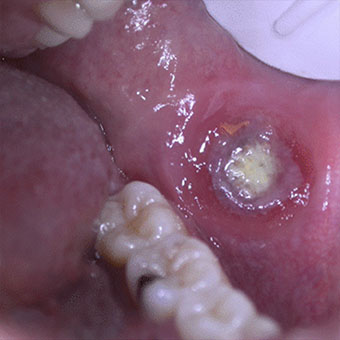
Manifestations stomatologiques et maxillofaciales de l'infection par le virus de l'immunodéficience humaine
Par L. Benslama, W. Hasni.
Les manifestations stomatologiques sont constantes au cours de l'infection par le virus de l'immunodéficience humaine (VIH). Leurs expressions cliniques et leur importance dépendent de l'évolution de l'infection, et sont majeures au stade de syndrome d'immunodéficience acquise (sida). Elles sont principalement infectieuses, tumorales et, depuis quelques années, iatrogènes. Les infections sont surtout fongiques (candidoses), virales (herpès, zona, infections à papillomavirus humains, etc.), moins souvent bactériennes (streptococcies).
Les maladies sexuellement transmissibles, en particulier la syphilis, sont en recrudescence préoccupante. Les principales tumeurs sont celles de la maladie de Kaposi (MK). Les intolérances médicamenteuses sont fréquentes et sont d'expression surtout dermatologique mais également stomatologique (syndromes de Stevens-Johnson et de Lyell), observées avec les sulfamides et certains antirétroviraux (ART).
L'utilisation de thérapeutiques antirétrovirales hautement efficaces et prolongées (highly active antiretroviral therapy [HAART]) a entraîné une baisse de l'incidence de la plupart des pathologies opportunistes, complications infectieuses et tumorales (sauf les verrues buccales multiples et le zona). Elle s'est traduite par certaines conséquences comme le syndrome lipodystrophique (signes d'atrophie périphérique et d'hypertrophie centrale associés à des degrés divers avec un syndrome métabolique). L'allongement de la survie et les nouvelles méthodes de prophylaxie des infections opportunistes ont progressivement modifié les stratégies diagnostiques et thérapeutiques des manifestations stomatologiques de l'infection par le VIH.
Mots-clés : Virus de l'immunodéficience humaine, Manifestations stomatologiques
The full text of this article is available in PDF format.
Voir + : Manifestations stomatologiques et maxillofaciales de l'infection par le VIH / EMC - Chirurgie orale et maxillo-faciale 2019
Pathologies médicales potentiellement malignes de la muqueuse buccale
Par L. Benslama
Malgré l'exérèse chirurgicale et la surveillance, la transformation maligne est toujours possible
- Qu'est-ce qu'une lésion potentiellement maligne ? Les termes "précancéreux", "précurseur", "prémalin", "néoplasie intra-épithéliale" et "potentiellement malin" ne sont plus adéquats pour décrire des aspects cliniques supposés se dérouler en deux ou plusieurs étapes, alors qu'il est peu probable qu'il y ait une même et unique voie de cancérisation semblable pour tous les individus.
Le terme consensuel retenu est "lésion ou affection potentiellement maligne". Il suffit à recouvrir toutes les situations rencontrées.
- Leucoplasie :
D'après la définition aujourd'hui retenue, une leuco- plasie est une lésion blanche à risque discutable de cancérisation après exclusion de toutes les lésions ou affections n'ayant pas un risque accru pour le cancer. La leucoplasie est un terme purement clinique et n'a aucune spécificité histologique.
Voir + : Pathologies médicales potentiellement malignes de la muqueuse buccale / La Revue du praticien. Octobre 2019
Bouche et médicaments
Par L. Benslama
De nombreux effets indésirables : bouche sèche, aphtes, lichen plan, érythème polymorphe, angiœdème, candidoses…
Le développement de nouveaux médicaments apporte régulièrement de nouveaux signalements d'effets indésirables et d'interactions médicamenteuses. L'iatrogénie (maladies ou troubles physiques liés à un traitement ou à un médicament) devient omniprésente, et la bouche est le lieu d'expression de nombre d'entre elles.
Bouche sèche
La sécrétion salivaire est assurée par trois paires de glandes principales, parotides, submandibulaires et sublinguales, et par un grand nombre de glandes salivaires accessoires, réparties dans la muqueuse orale et pharyngée. De nombreux médicaments sont susceptibles d’entraîner une sécheresse buccale, en particulier chez le sujet âgé.
Aphtes et ulcérations buccales
Les aphtes et ulcérations médicamenteuses sont à distinguer des ulcérations buccales caustiques induites par un contact direct du médicament sur la muqueuse (aspirine, desloratadine, bisphosphonates) résultant le plus souvent d’un mésusage ou d’automédications (phénols, eugénol, peroxyde d’hydrogène).
Hypertrophie gingivale
Trois familles de médicaments sont à l’origine d’hypertrophies gingivales : la phénytoïne, les immunosuppresseurs et les inhibiteurs calciques.
Phénytoïne.
Les hypertrophies gingivales associées à l’administration de phénytoïne (Di-Hydan, Dilantin, Diphantoïne) sont connues depuis plus de 60 ans...
Voir + : Bouche et médicaments / La Revue du praticien. Octobre 2019
Kimura's disease of the hard palate
Benslama L, Labrousse D, Gruffaz F, Goudot P.
PubMed
Rev Stomatol Chir Maxillofac Chir Orale. 2016 Apr;117(2):101-3. doi: 10.1016/j.revsto.2016.01.004. Epub 2016 Mar 7.
Abstract
INTRODUCTION :
Kimura's disease is an inflammatory and autoimmune disease that is endemic in Middle East and Asian countries but remains rare in Europe. It usually presents as subcutaneous nodules combined with cervical lymphadenopathies in the cervicofacial region. The oral mucosa localization is extremely rare. We report for the first time a case of hard palate localization.
OBSERVATION :
A 61-year-old male patient from Martinique consulted for a recent median, extensive and poorly defined black area localized on the hard palate. It was painless and did not cause any discomfort. We performed a biopsy to rule out a melanoma. The pathology report led to diagnosing Kimura's disease. The biological parameters, especially the renal status, were normal. A simple medical supervision was prescribed.
DISCUSSION :
This was the first time Kimura's disease was observed as a pigmented area located on the hard palate. The diagnosis of melanoma first had to be ruled out. The histological and immunohistological parameters are mandatory to make a diagnosis.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Masson SAS. All rights reserved.
KEYWORDS :
Kimura's disease; Maladie de Kimura; Muqueuse orale; Oral mucosa; Palais; Palate
Voir + : Kimura's disease of the hard palate / Rev Stomatol Chir Maxillofac Chir Orale. 2016 Apr
Oral pain
Benslama L.
Pain, a major symptom of stomatological disease, usually leads to a specialist consultation. Most commonly it is caused by dental caries and differs in nature and in intensity according to the stage of disease: dentinitis, pulpitis, desmodontitis and dental abscess. Added to this is peridental pain and the pre- and post-operative pains related to these diseases. Almost all oral-maxillary pathology is painful, be it boney such as in osteomyelitis and fractures, mucosal in gingivo-stomatitis and aphthous ulcers, or tumourous. However, besides the "multidisciplinary" facial pains such as facial neuralgia and vascular pain, two pain syndromes are specific to stomatology: pain of the tempero-mandibular joint associated with problems of the bite and glossodynia, a very common somatic expression of psychological problems.
Voir + : Oral pain / Rev Prat. 2002 Feb
Infectious stomatitis
Agbo-Godeau S., Benslama L..
Infectious stomatitis is bacterial essentially when of dental origin, the viral forms most often causing a vesicular and erosive stomatitis, and fungal secondary to a modification of the oral commensal flora. The diagnosis is often clinical with the lesions being of characteristic appearance and arising in a suggestive context. When the appearance is less typical or when the choice of treatment necessitates the identification of the germ, specific samples are taken. The treatment of viral stomatitis is essentially symptomatic, that of bacterial and fungal stomatitis comprising two arms: the specific treatment of the acute episode and then that of the particular oral-dental terrain.
Voir + : Infectious stomatitis / Rev Prat. 2002 Feb 15
Carcinoma of the lips
Benslama L..
Epidermoid carcinoma, that is, squamous cell carcinoma of the skin, is the most common malignant tumor of the lips. It occurs especially in men. Its primary causes are sun exposure, smoking, and chronic irritation. Leukoplakia is the most frequent precancerous lesion. Epidermoid carcinoma may appear clinically as a scaly erosion or an ulceration. Standard treatment is surgical excision with reconstruction.
Voir + : Carcinoma of the lips / Presse Med. 2008 Oct
Fatty tumors of the jaws
Ben Slama L, Landoulsi Helal A, Fodha Ben Jilani H, Zairi I, Adouani A..
Intraosseous lipoma is a benign tumor of the bone. It is mostly seen in the metaphyses of the long bones and calcaneus. There are few documented cases of intraosseous lipomas in the jaw. Clinically, the lesion is usually silent and radiologically it appears as a radiolucent area rarely including some radio-opacities. Diagnosis is based on clinical, radiological and histopathological features. Surgical removal of the lesion is the recommended treatment.
Copyright © 2014. Published by Elsevier Masson SAS.
Voir + : Fatty tumors of the jaws/ Rev Stomatol Chir Maxillofac Chir Orale. 2014 Feb
Nasopalatine duct cyst
Ben Slama L, Zoghbani A, Hidaya S..
The nasopalatine cyst is the most common epithelial and non-odontogenic cyst of the maxilla. It is of embryological origin. It is different from a radicular cyst. The diagnosis is based on radiographic and histological data. The treatment is enucleation. The surgical approach depends on the size of the cyst and its anterior or posterior extension. Excision must be total to avoid relapse which may occur beyond 5 years. Long-term follow-up is essential.
Voir + : Nasopalatine duct cyst / Rev Stomatol Chir Maxillofac. 2009 Nov
Potentially malignant disorders of the oral mucosa: terminology and classification
Benslama L.
The last WHO expert workgroup recommended abandoning the distinction between potentially malignant lesions and conditions. The term to use is "potentially malignant disorders". Leukoplakia is the most common of these disorders, while erythroplakia is rather rare. The diagnosis is still made by excluding other documented white or red lesions. Despite progress in molecular biology, no marker allows predicting malignant transformation. These lesions are treated surgically with or without dysplasia. It is unknown if this surgery can really prevent transformation into squamous cell carcinoma. The potential malignancy of oral lichen planus is still debated. The risk of malignant transformation is lower than that of leukoplakia. No treatment may prevent this. Other potentially malignant conditions such as oral submucous fibrosis, actinic cheilitis, lupus, and immunodeficiency are rare.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Masson SAS. All rights reserved.
Voir + : Potentially malignant disorders of the oral mucosa: terminology and classification / Rev Stomatol Chir Maxillofac. 2010 Sep
Nasolabial cyst
Ben Slama L, Zaghbani A, Hidaya S.
Nasolabial cyst is a rare epithelial and non-odontogenic cyst of the jaw. It is situated behind the ala nasi, extending backwards into the inferior nasal meatus and forward into the labio-gingival sulcus. Predominant symptoms are swelling of the nasal vestibule, local pain, and nasal obstruction. Radiology is not specific and CT scan may be contributive. Surgical excision is the first line treatment; it proves the diagnosis and prevents recurrence.
Voir + : Nasolabial cyst / Rev Stomatol Chir Maxillofac. 2010 Apr
Osteoradionecrosis and dental implants
Ben Slama L, Hasni W, De Labrouhe C, Bado F, Bertrand JC..
INTRODUCTION:
Osteoradionecrosis (ORN) is a severe complication of radiation therapy (RT). A triggering factor is frequently present. It is often a dental, periodental, or surgical traumatism. We report the case of a bilateral ORN: the first lesion appeared 3months after the end of RT around the osteosynthesis plate and was treated by mandibular resection. The second lesion appeared 40months after RT on the opposite side, due to peri-implantitis. Dental implants had been inserted 10years before cancer therapy. No case of ORN in post-implantation RT had been previously reported.
CASE REPORT:
A 75-year-old woman was admitted for a squamous cell carcinoma of the right cheek extending to the intermaxillary commissure, the maxillary tuberosity, the soft palate, the lingual junction, and the vestibule up to the second premolar area. There was no suspicious lymph node. She had undergone dental implant procedure 15 and 10 years before, respectively, one in the second premolar position of the right maxilla and four in the premolar and molar left mandible area. All of them were osseo-integrated and charged. A trans-mandibular buccopharyngectomy with modified radical neck dissection was performed, completed by RT. The total dose of irradiation was 65Gy in the oral cavity and 45Gy on cervical and supraclavicular areas. Delayed mucosal healing was observed on the right mandible and ORN appeared in this area 3months after the end of irradiation. Mandibular resection was necessary. Later, the right maxillary implant was lost, and multiple dental extractions were required. Forty months after RT, peri-implantitis was observed on the left side of the mandible, complicated by ORN and pathological fracture. No surgical reconstruction could be performed because of the patient's age and state. The patient was carrying a complete removable maxillary prosthesis on latest follow-up.
DISCUSSION:
This was the first case of ORN on dental implants placed before RT. RT is a risk factor of implant failure, a relatively rare and unpredictable event. Most often, it causes implant loss and exceptionally ORN. In our case, ORN was bilateral. The first lesion was probably due to surgical trauma. The second one, on the opposite side, was caused by peri-implantitis. Irradiation overdose on the alveolar mandibular ridge, close to the implant, may have been the cause. In our case, there was no severe pain, and slow evolution led to a pathological fracture.
Voir + : Osteoradionecrosis and dental implants / Rev Stomatol Chir Maxillofac. 2008 Dec
Diseases of the oral mucosa. Neuroma
Benslama L.
No abstract available.
Voir + : Diseases of the oral mucosa. Neuroma / Rev Stomatol Chir Maxillofac. 2004 Sep
Pleomorphic adenoma of the parotid gland]
Paranque AR, Breton P, Ben Slama L, Bertrand JCh, Goga D..
Voir + : Pleomorphic adenoma of the parotid gland] / Rev Stomatol Chir Maxillofac. 2002 Feb
Precancerous lesions of the buccal mucosa
Benslama L..
OBJECTIVES:
We analyzed data in the literature in comparison with experience at the Department of Cancer and Oral pathology of the Stomatology and Maxillo-Facial Surgery division of la Salpêtrière Hospital on precancerous lesions of the oral mucosa, in order to establish definitions and describe epidemiological, clinical, histological findings as well as natural history and treatment outcome.
MATERIAL AND METHODS:
Three literature sources were analyzed: Medline and Current Contents searches, books and references listed in articles. The following key words were used and classed into three groups; 1) oral mucosa, epidemiology, precancerous lesions, malignant transformation, dysplasia, leucoplakia, oral lichen planus, erythroplasia, verrucous, cheilitis, candidosis, immunodepression, 2) oral mucosa, tumor markers, carcinogens, keratin, keratinocytes, gene, nuclear proteins, p53 protein, Ki-67 antigen, 3) oral mucosa, therapy, prevention, nutrients. The period chosen ran from 1980 to 1998. This automatic literature search was completed by systematic manual search of summaries in specialized journals published in 1997-1998. The lists of references in the identified articles were consulted and furnished the principal publications concerning precancerous lesions of the buccal mucosa. In all 383 references were selected and analyzed by level of scientific proof. Among these 135 are cited in the text. If data in the literature were insufficient, the physicians at the Department of Cancer and Oral pathology of the Stomatology and Maxillo-Facial Surgery division of La Salpêtrière Hospital were consulted to provide their experience-based recommendations.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION:
Clear and practical definitions drawn from current knowledge were adopted. Precancerous lesions were distinguished from precancerous states. Precancerous lesions included chronic lesions of the oral cavity on which cancer of the oral cavity is known to develop. These were: leucoplakia, oral lichen planus, erythroplasia, papillomatous lesions, actinic cheilitis, submucosal fibrosis, keratotic candidosis, and tertiary syphilis. The precancerous states included cancers occasionally observed in the oral cavity: immunodepression and Plummer Vinson syndrome were analyzed. Epidemiological, clinical, histological, and evolutive data as well as therapeutic strategies were described. A decisional algorithm was elaborated for leucoplakia. The text was enriched with images available in the Department.
CONCLUSION:
Precancerous lesions of the oral mucosa offer a particularly interesting area of research for understanding the process of cancer formation and its prevention. The level of scientific proof available in the large majority of the published reports is low. Few recent publications provide relevant data. In practice, the experience in the management of cancer and precancerous lesions of the oral mucosa accumulated over the last 40 years at the Department of Cancer and Oral pathology of the Stomatology and Maxillo-Facial Surgery division of la Salpêtrière Hospital provides an invaluable source of information.
Voir + : Precancerous lesions of the buccal mucosa / Rev Stomatol Chir Maxillofac. 2001 Apr
Jaw muscle tumors
Ben Slama L, Zaghbani A, Hidaya S.
Muscular tumors are rare. They hardly ever present in jaws. Rhabdomyoma have never been reported in this localization. Clinical and radiological features are non-specific. The diagnosis is based on histopathological features. It is difficult to make for leiomyosarcoma. Surgical excision is the recommended treatment, conservative for leiomyoma, radical for other malignant tumors. Rhabdomyosarcoma has a good prognosis unlike leiomyosarcoma.
Voir + : Jaw muscle tumors / Rev Stomatol Chir Maxillofac. 2010 Apr
Langerhans cell histiocytosis
Ben Slama L, Ruhin B, Zoghbani A.
Langerhans cell histiocytosis (ex histiocytosis X) is usually present in children. It is a clonal proliferation of non-functional Langerhans's cells. Histological aspects are variable. The diagnosis is made in immunolabeling by anti-CD1a. Clinical presentations are variable, depending on their extension. Three syndromes are actually the same pathogenic process: eosinophilic granuloma (single or multiple osseous localizations), Hand-Schüller-Christian disease (chronic form with bone and visceral dissemination) and Abt-Letterer-Siwe disease (disseminated and acute malignant presentation).
Voir + : Langerhans cell histiocytosis
Potentially malignant character of oral lichen planus and lichenoid lesions
Mares S, Ben Slama L, Gruffaz F, Goudot P, Bertolus C.
INTRODUCTION:
Many authors have reported the possible malignant transformation of oral lichen. The incidence of this event remains controversial. Many authors make a distinction between the "true" oral lichen planus (OLP) and lichenoid lesions (LL) according to the WHO clinical and histological classification. For these authors an increased risk of development of oral cancer could occur only on LL. Our aim was to check this hypothesis on a cohort followed for 10 years.
MATERIAL AND METHODS:
We included patients who were referred to our team for the first time between 1995 and 1997, still followed in 2010, with a histological diagnosis of buccal lichen planus. We classified lesions as OLP or LL according to the WHO clinical and histological classification: the two clinical criteria for OLP were a reticulated aspect and bilateral and symmetric lesions. Three histological criteria were necessary for the diagnosis: dense inflammatory infiltrate in the upper lamina propria, liquefaction degeneration of basal keratinocytes, and no signs of dysplasia. The final diagnosis was OLP, when all clinical ad histological criteria were met otherwise it was LL. We studied the patient's outcome between their first consultations and May 2010.
RESULTS:
Thirty-two patients, whose data was available, met inclusion criteria. Eight were diagnosed with OLP and 24 with LL. The mean follow-up was 164 months [154-183]. No oral cancer was observed in the OLP group. Two patients in the LL group presented with oral cancer after 45 and 143 months of follow-up.
DISCUSSION:
Malignant transformations were observed only in the LL group. Our results correlate with those of Van Der Meij et al. published in 2006. The strict use of the WHO diagnostic criteria seems to allow identifying patients at risk of developing oral cancer (LL) and others with only a benign course of this chronic oral mucosal disease. These results need to be confirmed by prospective multicentric studies.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Masson SAS. All rights reserved.
KEYWORDS:
Lichen plan buccal; Neoplastic cell transformation; Oral lichen planus; Transformation maligne
Voir + : Potentially malignant character of oral lichen planus and lichenoid lesions / Rev Stomatol Chir Maxillofac Chir Orale. 2013 Nov
Reconstruction of the tip of the nose
Breton P, Ben Slama L, Boolauck SJ, Guyot L, Laure B.
Voir + : Reconstruction of the tip of the nose / Rev Stomatol Chir Maxillofac. 2005 Apr
Desmoplastic fibroma
Ben Slama L, Zaghbani A, Hidaya S, Ruhin B.
Desmoplastic fibroma is a rare benign intraosseous neoplasms. They can affect the jaw. Posterior mandibular bone involvement is the most frequent localization. They are locally aggressive and recurrence is frequent. Radioclinical signs are not specific and the histological diagnosis may be difficult. Extended surgical removal is the recommended treatment.
Voir + : Desmoplastic fibroma / Rev Stomatol Chir Maxillofac. 2010 Apr
Miconazole in gingival muco-adhesive tablet (Loramyc 50mg)
Ben Slama L, Hasni W.
Voir + : Miconazole in gingival muco-adhesive tablet (Loramyc 50mg) / Rev Stomatol Chir Maxillofac. 2008 Jun
Cat-scratch disease localisation in the parotid gland
Ben Slama L, Hasni W, Royer B.
INTRODUCTION:
Cat scratch disease is an infection due to Bartonella henselae. It is one of the principal causes of benign chronic adenopathy in children or young adults.
CASE REPORT:
A 36-year-old woman presented with a left parotid pre-auricular swelling suggesting a pleiomorphic adenoma. The history and complementary tests (ultra sonography, MRI, cytopuncture, B. henselae serology) led to a diagnosis of cat scratch disease. Doxycilline was efficient within 15 days.
DISCUSSION:
The parotid localization of cat scratch disease is very rare. When a patient presents with parotid swelling, the distinction between a tumor and lymph node is not easy. Performing complementary tests can be in balance with a quicker but sometimes inappropriate surgical indication. The diagnosis is made even more difficult because of delayed specific serologic tests as for B. henselae.
Voir + : Cat-scratch disease localisation in the parotid gland / Rev Stomatol Chir Maxillofac. 2008 Jun
Mucosal lymphomatoid papulosis: 2 cases
Benslama L, Andre CV, Charlotte F, Agbo-Godeau S, Goudot P.
BACKGROUND:
Lymphomatoid Papulosis (LP) is a chronic dermatosis progressing by flare-up. According to the WHO-EORTC classification, LP is a form of CD30+ primitive cutaneous lympho-proliferation. Mucosal lesions are rare, with 15 published cases. We report two new cases of oral localizations, without any cutaneous involvement.
PATIENTS AND METHODS:
Two women, 32 and 63 years old, presented with an isolated painful oral ulceration, of the maxillary tuberosity and of the inner side of the cheek respectively. The general state of health was preserved. Immunohistochimical analysis of the biopsies showed two Type A LPs. Lesions spontaneously resolved.
DISCUSSION:
Among the rare published cases, oral localization involved exclusively the tongue and the labial mucosa and almost all patients presented with previous cutaneous lesions. Isolated maxillary tuberosity or cheek involvements were not described yet.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Masson SAS. All rights reserved.
KEYWORDS:
Lymphomatoid papulosis; Papulose lymphomatoïde
Voir + : Mucosal lymphomatoid papulosis / Rev Stomatol Chir Maxillofac Chir Orale. 2015 Apr
Listerine
Benslama L.
Voir + : Listerine / Rev Stomatol Chir Maxillofac. 2006 Feb
Où allons-nous avec les bisphosphonates ?
Benslama L..
Voir + : Où allons-nous avec les bisphosphonates ? / Revue de Stomatologie et de Chirurgie Maxillo-faciale. Volume 107, Issue 6, December 2006
Antiseptiques buccaux
L.Ben Slama. M.Djemil
Les antiseptiques désignent des produits destinés à l’antisepsie des tissus vivants (peau saine, muqueuses, plaies etc.). Ils ont le statut de médicament, contrairement auxdésinfectants, appellation destinée aux milieux inertes (dispositifs médicaux, sols, surfaces) et aux produits d’hygiène corporelle. Les "produits pour l’antisepsie des mains " sont spécifiquement destinés à cet usage. Selon son mode d'utilisation, un produit peut être antiseptique ou désinfectant.
Ces produits ou procédés ont en commun la capacité d’inactiver ou de tuer les micro-organismes, y compris les virus, afin d’enrayer, par bactériostase ou bactériocidie, la pullulation des germes pathogènes responsables desinfections primitives ou secondaires. D’usage externe, leur action est momentanée, une nouvelle contaminationétant toujours possible. Les antibiotiques répondent aussi à cette définition, mais sont réservés à d’autres usages, notamment en raison de la lenteur de leur action lors d’une application locale.
Voir + : Antiseptiques buccaux : Rev. Stomatol. Chir. Maxillofac., 2004; 105, 4, 231-234© Masson, Paris, 2004.
Aphthae and aphthosis
Benslama L.
Voir + : Aphthae and aphthosis / Rev Stomatol Chir Maxillofac. 2003 Oct
Anti-inflammatory and repair activity of two toothpastes in an ex-vivo human gingival mucosa model
Boisnic S, Ben Slama L, Branchet-Gumila MC.
INTRODUCTION:
Our aim was to compare the anti-inflammatory activity of two toothpastes, one including enoxolone 1%, the other including plant extracts and sodium bicarbonate.
MATERIAL AND METHODS:
Gingival fragments were kept alive ex-vivo. Inflammation, inflammatory mediators (SP and LPS) were applied to culture medium on contact with corium to induce inflammation. The effect of both toothpastes was assessed with histological and biochemical parameters (inflammatory cytokine IL8) of inflammation on the synthesis of collagen and cellular viability.
RESULTS:
Both toothpaste "A" including enoxolone at 1% and "P" including plant extracts and sodium bicarbonate were effective on edema and vasodilatation. "A" acted on IL8 synthesis, unlike "P". Both toothpastes boosted collagen synthesis by fibroblasts. The percentage of cellular viability for "A" was superior to the currently admitted standard (80%), unlike to "P".
DISCUSSION:
The mechanisms of action of each toothpaste seem to be different. "A" modulates pro-inflammatory cytokine IL8 expression, unlike "P". The toothpaste "A" seems to be better tolerated.
Voir + : Anti-inflammatory and repair activity of two toothpastes in an ex-vivo human gingival mucosa model / Rev Stomatol Chir Maxillofac. 2010 Nov-Dec
Long-term effectiveness and side effects of mandibular advancement devices on dental and skeletal parameters.
Vigié du Cayla G, Collet JM, Attali V, Kerbrat JB, Benslama L, Goudot P.
INTRODUCTION:
Continuous positive airways pressure, generally used to treat obstructive sleep apnea-hypopnea syndrome (OSAHS), is not tolerated well by many patients. An alternative is to treat OSAHS with mandibular advancement devices (MAD). This research assesses the long term (> 2 years) effectiveness and the side effects on dental and skeletal parameters of these devices.
MATERIAL AND METHODS:
We selected 24 patients with moderate to severe OSAHS. All were treated with MADs for at least 2 years. We gathered cephalometric teleradiographs in centric relation and sleep recordings before and after the patients were treated. We evaluated the patients' apnea-hypopnea indexes (AHI) as well as their Epworth sleepiness scale (ESS) scores. We measured the inclination of the central incisors and the positions of the upper and lower jaws.
RESULTS:
Mandibular advancement devices were used for more than 2 years (3.9 ± 1.9 years). We observed a statistically significant decrease of the patients' AHI and their ESS scores. We also observed a modification of the inclination of the lower central incisors (+0.521; P = 0.047) and of the position of the maxilla (-0.287; P = 0.039).
DISCUSSION:
We demonstrated the clinical effectiveness of mandibular advancement devices for treating OSAHS, with a very low rate of side effects on dental and skeletal positions.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Masson SAS. All rights reserved.
KEYWORDS:
Mandibular advancement; Obstructive sleep apnea; Side effects
Voir + : Long-term effectiveness and side effects of mandibular advancement devices on dental and skeletal parameters. / J Stomatol Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2019 Feb
Topical retinaldehyde treatment in oral lichen planus and leukoplakia.
Boisnic S, Licu D, Ben Slama L, Branchet-Gumila MC, Szpirglas H, Dupuy P.
The aim of this exploratory study was to assess the efficacy of a natural metabolite of vitamin A, retinaldehyde 0.1%, vehicled in a gel in 17 patients with oral lichen planus and in 13 patients with oral leukoplakia, twice daily for 2 months. Our investigation was clinical, histological, immunohistochemical through the expression of markers of cell terminal differentiation and biochemical by using two-dimensional gel electrophoresis of cytokeratins (CK). In addition, the activity of retinaldehyde was studied ex vivo on surviving buccal mucosa. Retinaldehyde gel 0.1% showed good clinical efficacy, resulting in 6% disappearance and 82% improvement of the lesions in lichen planus and 17% disappearance and 75% improvement in leukoplakia. This was confirmed with immunohistochemistry, which revealed down-regulation of filaggrin and CK-10 as markers of terminal differentiation in both diseases. The effects of retinaldehyde in these two diseases were further demonstrated in the ex vivo surviving mucosal model, resulting in histological disappearance of keratinization in 80% of the lichen planus fragments and 40% of the leukoplakia fragments, associated with down-regulation of filaggrin and CK-10.
Voir + : Topical retinaldehyde treatment in oral lichen planus and leukoplakia. / Int J Tissue React. 2002
Topical tretinoin in the treatment of lichen planus and leukoplakia of the oral mucosa. A biochemical evaluation of the keratinization
Branchet MC, Boisnic S, Pascal F, Ben Slama L, Rostin M, Szpirglas H..
In earlier work, we demonstrated that 0.1 p. 100 topical tretinoin is clinically effective and well tolerated compared with placebo for the treatment of oral leukoplakia and oral keratosic or erythematous lichen planus. Here we aimed to complete this clinical protocol with histological and biochemical analyses comparing the biopsy specimens collected at inclusion and those collected after 4 months of treatment. Histological results were based on changes in keratinization observed between onset of treatment and 4 months treatment. Biochemical studies included the use of antibodies (anti-cytokeratins 10-11, anti-filaggrine) for the immunohistochemical evaluation of keratinization and 2-dimensional gel electrophoresis for measuring cytokeratins. In patients with lichen planus, histological changes during treatment showed that, in the 10 patients in the tretinoin group, keratinization disappeared in 6 and decreased significantly in 3. Immunohistochemistry revealed that cytokeratins 10-11 and filaggrin disappeared in 57 p. 100 of the patients treated with tretinoin versus 25 p. 100 in the patients given placebo. Bidimensional gel electrophoresis showed that cytokeratins 1, 2, 10 and 11 disappeared only in the tretinoin group (60 p. 100 of the cases). In patients with leukoplakia, histological changes during treatment showed that, in the tretinoin group, keratinization disappeared in 5 cases and decreased in 5 others. Immunohistochemistry revealed that cytokeratins 10-11 disappeared in 30 p. 100 of the patients treated with tretinoin versus 25 p. 100 in the placebo group. Bidimensional electrophoresis demonstrated that cytokeratins 1, 2, 10 and 11 disappeared in 43 p. 100 of the patients treated with tretinoin.
Voir + : Topical tretinoin in the treatment of lichen planus and leukoplakia of the oral mucosa. A biochemical evaluation of the keratinization / Ann Dermatol Venereol. 1994
Topical tretinoin in the treatment of lichen planus and leukoplakia of the mouth mucosa. A clinical evaluation
Boisnic S, Branchet MC, Pascal F, Ben Slama L, Rostin M, Szpirglas H.
A randomized study was conducted to evaluate the effect of tretinoin and patient tolerance to treatment with topical applications in series of 20 cases of smoking-related or traumatic oral keratoses leukoplakia and of 20 cases of lichen planus. In each group, patients applied the topical ointment containing tretinoin (10 patients) or placebo (10 patients) twice daily. Clinical outcome was evaluated on the basis of the surface area of the lesion, measured monthly during treatment, as compared with the area observed at treatment onset. After 4 months treatment, there was a significant decrease in the surface area of the lesion in the patients with lichen planus (p < 0.02): 94 p. 100 in the tretinoin group versus 21.4 p. 100 in the placebo group. In patients with leukoplakias, there was also a very significant reduction in the surface area of the lesion after 4 months of treatment (p < 0.001): 80 p. 100 in the tretinoin group and 16 p. 100 in the placebo group. Tolerance to treatment was generally good despite a few complaints of quite temporary burning sensation at application rapidly resolutive.
Voir + : Topical tretinoin in the treatment of lichen planus and leukoplakia of the mouth mucosa. A clinical evaluation
Pilocarpin
Ben Slama L, Djemil M.
Voir + : Pilocarpin
Le prix de la rédaction 2010. The 2010 Editor's award
Benslama L..
Voir + : Le prix de la rédaction 2010. The 2010 Editor's award / Copyright © 2010 Published by Elsevier Masson SAS
Wound healing effect of Eludril in a model of human gingival mucosa
Boisnic S, Ben Slama L, Branchet-Gumila MC, Watts M, d'Arros G.
INTRODUCTION:
The aim of this study was to evaluate and to compare the potential for wound healing of the buccal mucosa with the use of two mouth rinses; one containing 0.10% chlorhexidine with alcohol, the second containing 0.12% chlorhexidine without alcohol.
MATERIAL AND METHOD:
Using a model of human buccal mucosa kept alive ex vivo, an immunohistochemical assessment of the mitotic potential of epithelial cells and a biochemical evaluation of the capacity of the fibroblasts of the gingival mucosa to synthesize collagen was performed.
RESULTS:
A mouth rinse containing 0.10% chlorhexidine with alcohol (Eludril) did not alter the potential for epithelial proliferation and for collagen synthesis within the gingival chorion grown in survival conditions. The results revealed a significant difference between the two mouth rinses for each of the parameters studied. The most favourable results were obtained with the mouth rinse containing alcohol.
DISCUSSION:
The presence of alcohol in a mouth rinse containing 0.10% chlorhexidine has no deleterious effects on healing capacity. On the contrary, it helps stimulate wound healing. The combination of chlorhexidine plus alcohol is superior for healing, chlorhexidine alone does not show any significant difference compared with the control.
Voir + : Wound healing effect of Eludril in a model of human gingival mucosa / Rev Stomatol Chir Maxillofac. 2006 Dec
Necrotizing sialometaplasia of the parotid gland associated with facial nerve paralysis.
Haen P, Ben Slama L, Goudot P, Schouman T.
INTRODUCTION:
Necrotizing sialometaplasia is a benign inflammatory lesion involving most frequently the minor salivary gland of the hard palate. Involvement of the parotid gland is rare, involvement of the parotid gland associated with facial palsy is exceptional.
CASE REPORT:
A 56-year-old male patient with Marfan syndrome presented with swelling and inflammation of the left parotid gland associated with progressively complete facial nerve paralysis. CT scan and MRI showed a parotid collection with hyper signal of the nearest tissues associated with erosion of the styloid process. A malignant tumor was suspected. The histological examination of a biopsy showed a lobulocentric process with necrosis, squamous metaplasia, and inflammation. The immunohistochemical examination supported a final diagnosis of necrotizing sialometaplasia.
DISCUSSION:
Necrotizing sialometaplasia of the parotid gland associated with facial nerve paralysis presents like a malignant neoplasm, both clinically and histologically. Only advanced immunohistochemical examination can really confirm the diagnosis.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Masson SAS. All rights reserved.
KEYWORDS:
Facial palsy; Necrotizing sialometaplasia; Parotid gland
Voir + : Necrotizing sialometaplasia of the parotid gland associated with facial nerve paralysis. / J Stomatol Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2017 Feb
Anti-inflammatory effect of enoxolone in an ex-vivo human gingival mucosa model
Boisnic S, Ben Slama L, Branchet-Gumila MC, Watts M, d'Arros G.
INTRODUCTION:
Our aim was to assess the modalities of use and the anti-inflammatory activity of enoxolone included in toothpaste and in a mouthwash solution.
MATERIAL AND METHODS:
We used gingival fragments kept alive during 3 days at 37 degrees C. To induce inflammation, inflammatory mediators (SP and LPS) were applied to culture medium on contact with corium. The toothpaste versus placebo was applied on epithelium, in double blind. Histological analysis was then performed on hematoxylin and eosin stained slides. Edema was evaluated with semi-quantitative scores. Vasodilatation was studied by counting the percentage of dilated vessels according to scores and the surface of these dilated vessels by morphometrical image analysis. An inflammatory cytokine, IL8, was measured in culture supernatants. Dosing IL1alpha tested the mouth solution.
RESULTS:
The toothpaste induced a significant decrease of edema, vasodilatation, and IL8 excretion. The enoxolone solution induced a decrease of IL1alpha.
DISCUSSION:
Enoxolone demonstrated an anti-inflammatory property whatever the carrier was.
Voir + : Anti-inflammatory effect of enoxolone in an ex-vivo human gingival mucosa model / Rev Stomatol Chir Maxillofac. 2010 Apr
A study model of the oral manifestations of HIV infection. The correlation and conformity of the WHO registry
Szpirglas H, Siegrist V, Benslama L.
Voir + : A study model of the oral manifestations of HIV infection. The correlation and conformity of the WHO registry / Rev Stomatol Chir Maxillofac. 1995
Management of mandibular ameloblastoma
Bouletreau P, Paranque AR, Steve M, Ranoarivony T, Chossegros C, Ruhin B, Ben Slama L, Rocton S, Bouvier S, Ernenwein D, Bertolus C, Rigolet A, Bertrand JC, Auriol M, Breton P.
Voir + : Management of mandibular ameloblastoma / Rev Stomatol Chir Maxillofac. 2006 Feb
Colchicine
Ben Slama L, Djemil M.
Voir + : Colchicine / Rev Stomatol Chir Maxillofac. 2002 Apr
Buccal lichen planus
Ben Slama L, Boisnic S, Samson J, Vaillant L, Fontès V, Francès C..
Voir + : Buccal lichen planus / Rev Stomatol Chir Maxillofac. 2002 Nov
Contribution of Parodium gel in an experimental model of human gingival inflammation
Boisnic S, Ben Slama L, Branchet-Gumila MC, d'Arros G.
INTRODUCTION:
Our aim was to evaluate the effect of a gingival gel containing chlorhexidine and Rheum Palmatum extract on gingival fragments stimulated by SP (substance P) and lipopolysaccharides (LPS).
MATERIALS AND METHODS:
Gingival fragments were maintained in survival for 3 days at 37 degrees C. To induce inflammation, SP and LPS were applied to the culture medium in contact with the corium. The gingival gel was applied on epithelium. Histological analysis was then performed on hematoxylin and eosin stained slides. Edema was evaluated with semi-quantitative scores. Vasodilation was studied by counting the percent of dilated vessels according to scores and the surface of these dilated vessels by morphometrical image analysis. An inflammatory cytokine, IL8, was measured in culture supernatants. Immunohistochemical expression of metalloproteinase type 9 (MMP9) implicated in inflammatory processes, was also studied (% of positive cells).
RESULTS:
Edema, vasodilation and IL8 were significantly increased after application of SP and LPS. Application of gingival gel showed a significant decrease of these parameters. A significant decrease of MMP9 on fibroblasts and mononuclear cells was observed after use of gingival gel.
Voir + : Contribution of Parodium gel in an experimental model of human gingival inflammation / Rev Stomatol Chir Maxillofac. 2003 Sep
Développement professionnel continu (DPC) : l’antibioprophylaxie / Continued professional development: Antibiotic prophylaxis
E. Varon, J.-P. Stahl, C. Strady, R. Gauzit, P.-Y. Blanchard, B. Gachot, L. Benslama.
Voir + : Développement professionnel continu (DPC) : l’antibioprophylaxie / Rev Stomatol Chir Maxillofac Chir Orale. 2013 Jun
On medical stomatology
Ben Slama L.
Voir + : On medical stomatology / Rev Stomatol Chir Maxillofac. 2002 Nov.
Diagnosis and treatment of nonodontogenic epithelial cysts. Apropos of 14 cases collected from the Oral Surgery Service of the University Hospital Center of Fann
Ndiaye FC, Ba A, Dia TS, Niang P, Diallo B, Benslama L.
Non odontogenic epithelial cyst, again called fissurary cyst, are dysembryophasic cyst of maxillary, they are born throughout the sutures line of faces. Their diagnosis is raising again association of clinic symptom, especially complementary examination and in particular dental vitality test. Their treatment is surgical. Around 14 cysts fissurary have been recorded in a seven-year period.
Voir + : Diagnosis and treatment of nonodontogenic epithelial cysts
Eosinophilic ulcer of the oral mucosa
Benslama L.
No abstract available.
Voir + : Eosinophilic ulcer of the oral mucosa
Human papillomavirus (HPV) induced lesions in HIV-positive individuals after highly active antiretroviral therapy
Benslama L.
Article in French
Voir + : Human papillomavirus (HPV) induced lesions in HIV-positive individuals after highly active antiretroviral therapy / Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2002 Apr
Synovial chondromatosis of the temporomandibular joint: Report and analysis of 12 cases.
Benslama L, Schouman T, Toure S, Chardain J, Goudot P.
OBJECTIVE:
We had for aim to study the clinical manifestations, diagnostic imaging techniques, histopathological and therapeutic findings of patients presenting with synovial chondromatosis (CS) of the temporomandibular joint (TMJ).
MATERIAL AND METHODS:
We reviewed the clinical history of all our patients who were diagnosed with CS between 2009 and 2013.
RESULTS:
We identified 12 cases of TMJ-CS, in 4 male and 8 female patients, with a mean aged of 50.5 years at diagnosis (range: 43-86 years). The average symptom duration prior to diagnosis was 11 months (range: 1-24 months). The most frequent clinical manifestations were joint pain (10 cases), restricted movement (6 cases), and swelling (4 cases). Panoramic radiographs were not contributive. CT scan and MRI findings led to a diagnosis in every case. 2 to 30 foreign bodies with various degrees of aggregation were removed by arthrotomy in our series and synovectomy was performed in all patients. These foreign bodies were in the upper compartment and the articular disk was not affected in 10 cases. A histopathological examination confirmed the diagnosis. The mean postoperative follow-up was 78 months. No case of chondrosarcoma was identified and the recurrence rate was low (1 case).
DISCUSSION:
The clinical manifestations of TMJ-CS are common and conventional imaging is poorly contributive so that the diagnosis is often late. The delay before diagnosis was an average11 months for our patients given our experience; it was almost twice longer in other series. Arthrotomy and excision of the loose bodies led to confirmation by histopathological analysis. Most of the time, this treatment is sufficient but long term clinical and radiological monitoring is required.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Masson SAS. All rights reserved.
KEYWORDS:
Synovial chondromatosis; Temporo-mandibular joint; Tumor
Voir + : Synovial chondromatosis of the temporomandibular joint / J Stomatol Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2019 Nov
Has the pharmaceutical industry forgotten about the oral cavity ?
Muster D, Ben Slama L.
Article in French
Voir + : Has the pharmaceutical industry forgotten about the oral cavity ? / Rev Stomatol Chir Maxillofac. 2006 Apr
Mandibular lymphoma
Vo Quang S, Sicard L, Samama M, Benslama L, Goudot P..
INTRODUCTION:
B-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma (B-LBL) rarely occurs in the oral cavity (3.5% of all intra-oral malignant tumors). Few cases of B-LBL mandibular bone involvement have been reported.
OBSERVATION:
We report the case of a 30-year-old female patient presenting with a single swelling of the left mandibular region, having grown for several weeks. Maxillo-facial CT and MRI showed inflammation of soft tissues and muscles without initial signs of osteitis, thus noncontributive to the diagnosis. A biopsy allowed diagnosing an intra-oral bone lymphoblastic lymphoma. The patient was referred to the hematooncology unit for treatment.
DISCUSSION:
Jaw localization of non Hodgkin's lymphoma is rare. Clinical symptomatology and radiological signs are poorly contributive. The diagnosis relies on a histopathological analysis.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Masson SAS. All rights reserved.
KEYWORDS:
Lymphoma; Mandibular
Voir + : Mandibular lymphoma
Human papillomavirus (HPV) induced lesions in HIV positive individuals after highly active antiretroviral therapy
Benslama L.
Article in French
Voir + : Human papillomavirus (HPV) induced lesions in HIV positive individuals after highly active antiretroviral therapy / Rev Stomatol Chir Maxillofac. 2002 Nov
Antifungal agents
Ben Slama L, Djemil M.
Article in French
Voir + : Antifungal agents
French Society of STomatology and Maxillo-facial Surgery: the mutation
Benslama L.
Article in French
Voir + : French Society of Stomatology and Maxillo-facial Surgery: the mutation / Rev Stomatol Chir Maxillofac. 2012 Sep
The 48th congress of the French Society of Stomatology, Maxillo-Facial Surgery, from 26 to 29th of September 2012 at Versailles
Benslama L.
Article in French
Voir + : The 48th congress of the French Society of Stomatology, Maxillo-Facial Surgery / Rev Stomatol Chir Maxillofac. 2012 Feb
Histochemical and biochemical modifications induced by experimental irradiation of human skin maintained in survival conditions and modulation by application of an emulsion containing trolamine. 2012
Boisnic S, Branchet-Gumila MC, Nizri D, Ben Slama L.
Radiotherapy continues to cause skin disorders. In this article, with the aid of our human skin model maintained in ex vivo survival conditions for 15 days, we describe the modifications caused by irradiation and their modulation by a trolamine-containing emulsion (Biafine). Normal human skin fragments were maintained in organ culture. One ionizing radiation session with 5 Gy was applied. Skin parameters were evaluated 24 h after the radiation session and were compared with a nonirradiated skin fragment: vascular modifications (histology), edema, epithelial proliferation, interleukin (IL)-1alpha and IL-6. Another series of skin fragments was maintained in survival conditions for 15 days after the radiation session to evaluate collagen neosynthesis by fibroblasts and any vascular changes (CD34). After irradiation the basal cell proliferation was reduced by approximately 50%. Extensive vasodilation occurred with altered capillary permeability accompanied by decreased CD34 transmembrane protein expression. Collagen synthesis and IL-1 secretion were increased. Biafine significantly reduced capillary alterations, restored CD34 expression as well as epithelial cell proliferation and significantly decreased collagen synthesis and IL-1 expression. With this ex vivo human skin model we confirmed the main modifications induced by radiotherapy as previously described in animal models: decreased basal cell proliferation and endothelial cell alterations and increased collagen synthesis by fibroblasts, probably under the influence of IL-1. The effect of Biafine emulsion on these histological and biochemical parameters may support its clinical efficacy.
Voir + : Histochemical and biochemical modifications... / Int J Tissue React. 2003
Autologous bone grafts, allografts and biomaterials
Benslama L.
Article in French
Voir + : Autologous bone grafts, allografts and biomaterials / Rev Stomatol Chir Maxillofac. 2005 Jun
Anterior pedicle temporalis muscle flap interposition in the treatment of TMJ disorders
Moreau A, Benassarou MA, Benslama L, Goudot P, Schoumann T.
Temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders are a common reason for consultation. Failure of medical treatments sometimes leads to the need for one of many surgical alternatives. Our purpose was to evaluate the results of anterior pedicle temporalis muscle flap interposition in the treatment of TMJ disorders.
MATERIAL AND METHODS:
For this prospective study, we selected 18 patients who underwent TMJ surgery involving the interposition of a temporalis muscle flap according to a standardized technique, between January 1, 2009 and August 31, 2014. CT imaging was performed on all patients prior to surgery. We documented the etiology of TMJ dysfunction, pre and postoperative pain using a visual analogue scale (VAS), pre and postoperative (last consultation) mouth opening, and complications. We used the Wilcoxon test for our statistical analysis.
RESULTS:
We observed a significant variation in preoperative and postoperative pain and mouth opening, with an average decrease in VAS values of 4.9/10 and an average increase of mouth opening of 11.1mm. No major complications were observed.
DISCUSSION:
The interposition of an anterior pedicle temporalis muscle flap in the treatment of temporomandibular joint disorder is a simple and effective technique.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Masson SAS. All rights reserved.
KEYWORDS:
Surgical procedure; Temporal muscle; Temporomandibular joint disorders
Voir + : Anterior pedicle temporalis muscle flap interposition in the treatment of TMJ disorders
Anti-nuclear and anti-smooth muscle antibodies in Caucasians, Africans and Asians with acute malaria
Daniel-Ribeiro C, Ben Slama L, Gentilini M.
In order to investigate whether or not a racial factor plays a role in modulating the pattern of autoimmune response associated with human malaria infection, we studied the frequencies of anti-nuclear (ANA) and anti-smooth muscle (SMA) antibodies in sera of 152 Caucasians, Africans and Asians with acute malaria. No significant differences were observed in the frequency of these autoantibodies (AAb) between malarial individuals of different racial groups even if we considered subjects of different races infected by the same plasmodial species (P. falciparum) and submitted to similar degrees of exposure to malaria infection, indicating that the pattern and frequency of the malaria induced AAb do not seem to be determined or modulated by racial factors.
Voir + : Anti-nuclear and anti-smooth muscle antibodies in Caucasians, Africans and Asians with acute malaria / J Clin Lab Immunol. 1991 Jul
The computer examined or the world of Big Blue and Apple
Dichamp J, Benslama L.
Article in French
Voir + : The computer examined or the world of Big Blue and Apple
Morbidity and mortality from ataxia-telangiectasia are associated with ATM genotype
Micol R, Ben Slama L, Suarez F, Le Mignot L, Beauté J, Mahlaoui N, Dubois d'Enghien C, Laugé A, Hall J, Couturier J, Vallée L, Delobel B, Rivier F, Nguyen K, Billette de Villemeur T, Stephan JL, Bordigoni P, Bertrand Y, Aladjidi N, Pedespan JM, Thomas C, Pellier I, Koenig M, Hermine O, Picard C, Moshous D, Neven B, Lanternier F, Blanche S, Tardieu M, Debré M, Fischer A, Stoppa-Lyonnet D; CEREDIH Network Investigators.
Collaborators (220)
BACKGROUND:
Ataxia-telangiectasia (A-T) is a rare genetic disease caused by germline biallelic mutations in the ataxia-telangiectasia mutated gene (ATM) that result in partial or complete loss of ATM expression or activity. The course of the disease is characterized by neurologic manifestations, infections, and cancers.
OBJECTIVE:
We studied A-T progression and investigated whether manifestations were associated with the ATM genotype.
METHODS:
We performed a retrospective cohort study in France of 240 patients with A-T born from 1954 to 2005 and analyzed ATM mutations in 184 patients, along with neurologic manifestations, infections, and cancers.
RESULTS:
Among patients with A-T, the Kaplan-Meier 20-year survival rate was 53.4%; the prognosis for these patients has not changed since 1954. Life expectancy was lower among patients with mutations in ATM that caused total loss of expression or function of the gene product (null mutations) compared with that seen in patients with hypomorphic mutations because of earlier onset of cancer (mainly hematologic malignancies). Cancer (hazard ratio, 2.7; 95% CI, 1.6-4.5) and respiratory tract infections (hazard ratio, 2.3; 95% CI, 1.4-3.8) were independently associated with mortality. Cancer (hazard ratio, 5.8; 95% CI, 2.9-11.6) was a major risk factor for mortality among patients with null mutations, whereas respiratory tract infections (hazard ratio, 4.1; 95% CI, 1.8-9.1) were the leading cause of death among patients with hypomorphic mutations.
CONCLUSION:
Morbidity and mortality among patients with A-T are associated with ATM genotype. This information could improve our prognostic ability and lead to adapted therapeutic strategies.
Copyright © 2011 American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology. Published by Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Voir + : Morbidity and mortality from ataxia-telangiectasia are associated with ATM genotype
Integrase mutants defective for interaction with LEDGF/p75 are impaired in chromosome tethering and HIV-1 replication
Emiliani S, Mousnier A, Busschots K, Maroun M, Van Maele B, Tempé D, Vandekerckhove L, Moisant F, Ben-Slama L, Witvrouw M, Christ F, Rain JC, Dargemont C, Debyser Z, Benarous R.
The insertion of a DNA copy of its RNA genome into a chromosome of the host cell is mediated by the viral integrase with the help of mostly uncharacterized cellular cofactors. We have recently described that the transcriptional co-activator LEDGF/p75 strongly interacts with HIV-1 integrase. Here we show that interaction of HIV-1 integrase with LEDGF/p75 is important for viral replication. Using multiple approaches including two-hybrid interaction studies, random and directed mutagenesis, we could demonstrate that HIV-1 virus harboring a single mutation that disrupts integrase-LEDGF/p75 interaction, resulted in defective HIV-1 replication. Furthermore, we found that LEDGF/p75 tethers HIV-1 integrase to chromosomes and that this interaction may be important for the integration process and the replication of HIV-1.
Voir + : Integrase mutants defective ... / J Biol Chem. 2005 Jul

